How K-Hospitals Pull Ahead: Korea’s Playbook for Fast, Practical Health Innovation
- AuthorElodie
- DateSep 19, 2025
- Views882
If you visited K-Hospital Fair (KHF) this year, you probably felt it: Korean hospitals don’t just pilot shiny tech—they operationalize it fast. From AI-ready EMRs to real-time patient telemetry and door-side digital boards, K-Hospitals keep finding pragmatic ways to deliver safer care with fewer clicks. What lets Korea pull ahead and move this quickly?
1) A financing and governance model built for scale
Korea runs a single, mandatory National Health Insurance (NHI) system covering virtually the entire population. Two institutions anchor the engine: the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) is the payer/insurer, while HIRA (Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service) reviews claims, sets/assesses reimbursement and quality, and connects nationwide health data for secondary use and policy improvement.

The result is strong national coverage with rapid diffusion potential when new standards or benefits are introduced. Korea’s health spending has also climbed into the upper OECD tier: health expenditure reached roughly 9.7–9.9% of GDP in 2022–2023, edging above the OECD average.
At the same time, Korea still relies more than peers on patient cost-sharing, with out-of-pocket (OOP) spending ~29% of total health expenditure—well above the OECD average. That gap has encouraged the growth of supplementary private health insurance (PHI), which reimburses co-pays and uncovered services; useful, but it can introduce utilization and equity trade-offs that policymakers watch closely.
2) Policy levers that turn innovation into everyday practice
Several national programs and standards push beyond pilots:
Reimbursement + standardization: MOHW and partners have used fee schedule pilots and EMR certification standards to drive safer, more connected records and to prepare datasets for secondary use and AI.
Smart Hospital support: Government “smart hospital” initiatives have annually funded projects that demonstrably improve patient safety and operational efficiency, accelerating adoption across reference sites.
Clear device/AI pathways: MFDS has issued guidance for machine-learning medical devices and (more recently) LLM-based clinical tools—clarifying when software is a medical device and how to evaluate it. Regulatory clarity shortens time-to-ward.
3) Fast, transparent procurement (나라장터 / KONEPS)
For public institutions, Korea’s KONEPS (나라장터) is a one-stop e-procurement system that handles everything from tender to payment. Vendors register once; hospitals can run open, electronic tenders with strong transparency and SME access—reducing friction and cycle time. (Private hospitals often procure directly, but KONEPS sets a high bar for efficiency.)
4) An ecosystem that prefers platforms over silos
Korean health-tech players increasingly join forces to avoid fragmented “cluster” tools and instead ship integrated, hospital-wide workflows. That’s the only way to lighten staff burden instead of adding logins and screens.
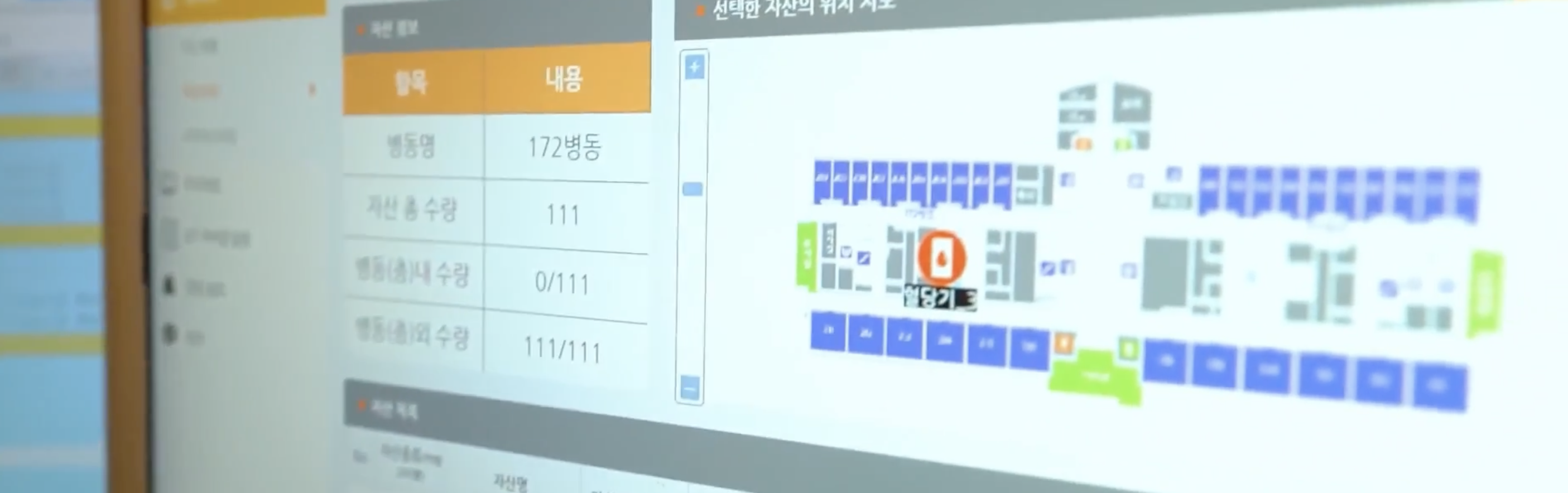
People & Technology’s foundation
At People & Technology, our roots lie in real-time location systems (RTLS) and smart sensing technologies. These capabilities allow hospitals to track patients, staff, and assets in real time, ensuring safety, efficiency, and visibility across the facility.
Building on this foundation, we are further expanding our digital healthcare software by partnering with specialized health-tech vendors to deliver a more comprehensive, integrative solution:
Continuous, remote vitals with partners ATsens, Nonin, and Mezoo: discrete, non-invasive patches and devices stream real-time vital signs whether patients are in bed or moving—directly into our platform’s live views and alerts.
EMR integration with EzCaretech: safe, fast exchange with the patient record so that what clinicians see is both current and clinically anchored.
Voice-driven workflows with PuzzleAI: hands-free note capture and voice control that let nurses keep eyes on patients, not keyboards.
At-the-door/bedside displays with SeeEyes (plus nurse call): room-level boards show the right data in real time and connect to call systems—closing the loop from detection to response.
Our goal isn’t to “win” a single niche—it’s to eliminate silos. Hospitals pick the modules and devices they need; the platform standardizes data, events, and alerts, so teams can adopt new tech without re-training every quarter. That’s how innovation feels like relief, not “one more system.”
5) Why foreign visitors at KHF notice the difference
Three features tend to stand out:
Operational realism: Projects are scoped to measurable improvements (falls, ED throughput, code response, bed turnover), not just proofs-of-concept. Funding follows outcomes.
Data plumbing first: EMR certification, HIRA data linkages, and MFDS guardrails arrive early, so AI/IoT layers have clean interfaces and governance.
Procurement that moves: e-tenders and standardized processes compress timelines while protecting transparency and competition.
6) The macro context: spending more—and smarter
Since 2010, Korea’s health spending has risen rapidly (from ~6% of GDP to ~9–10%), with gains linked to improved health outcomes. The mix of universal coverage, targeted smart-hospital grants, and evolving AI/EMR standards helps turn that spend into everyday value at the bedside.
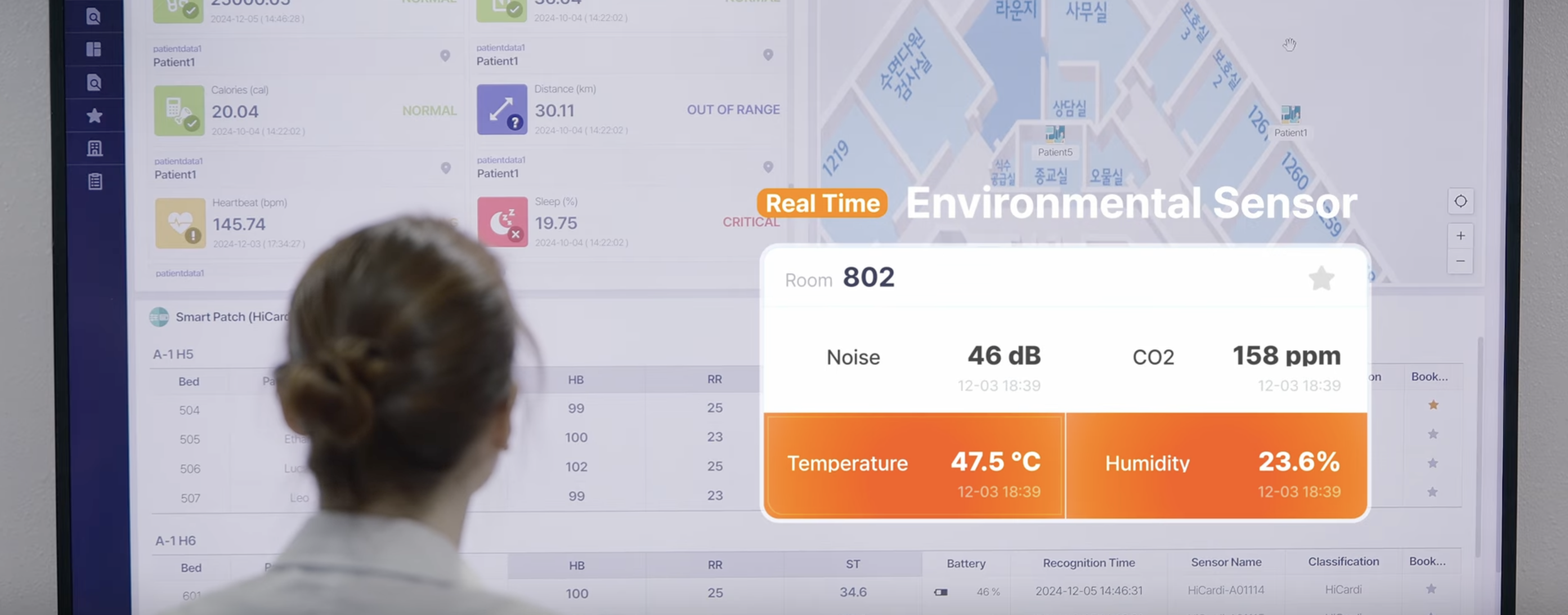
Our stance at People & Technology
There’s no need to reinvent the wheel. While some companies bet on a single “optimized” tool, we (and many Korean peers) are betting on the integrative platform that makes everything else interoperable—and thus, easier to adopt. Many partner technologies already ship with multilingual UIs and international certifications; others are advancing toward those marks. The point isn’t just exporting devices—it’s exporting joined-up care.
“Working together for a better future” isn’t just a slogan here; collaboration helped Korea transform from lower-income status into one of the world’s leading digital economies in a few decades. Health care is writing the next chapter—together.









